To consider an application for financing, fill out the form and send it to us by e-mail along with the project brief, or contact our experts
During a crisis, capital costs are usually lower than during periods of economic growth and higher resource prices.
It also becomes much cheaper to acquire companies and take over a ready-made business, the cost of which is definitely lower.
It would seem that during the economic crisis, investments are the main condition for the successful development and competitiveness of the company. However, in practice, enterprises refuse to invest, which is dictated by natural pessimism and fear for the safety of accumulated funds. In these difficult times, the concept of investment activity takes on a new meaning for business.
In general, any investment activity is primarily aimed at protecting and increasing capital.
An example is investing in securities, building large facilities, or acquiring promising companies early in the life cycle in order to generate high profits in the future.
Sedona Investments offers corporate clients a full range of financial and legal services related to investment activities.
Our professional team has helped many companies to implement investment projects in Europe, USA, Latin America, North Africa, the Middle East and other regions of the world. Contact us for details.
Physical investments: the essence of the investment process
According to the traditional concept, the investment activity of a business is characterized by the long-term investment of significant resources (usually exceeding the daily activities of the company) to generate profit and strengthen the competitive position in the future.Thus, the main purpose of investment is to obtain a certain competitive advantage by the enterprise or to prevent the loss of its position in the market.
These financial costs provide the business with a number of benefits in several areas at once:
• Economic advantages, which are expressed in increasing turnover, reducing operating costs, minimizing various risks of doing business, increasing the company's competitiveness.
• Social benefits, including improving the corporate culture, improving the personnel motivation system, identifying and integrating promising employees, training the team.
• Organizational benefits, which include increasing the company's ability to respond to current and future needs of the business environment, closing gaps in business organization, improving business processes.
Regardless of business goals, investment projects in the real sector usually lead to changes in production technology and service delivery, production potential, product quality or product range structure, which, in turn, is expressed in innovation, increased income or reduced costs.
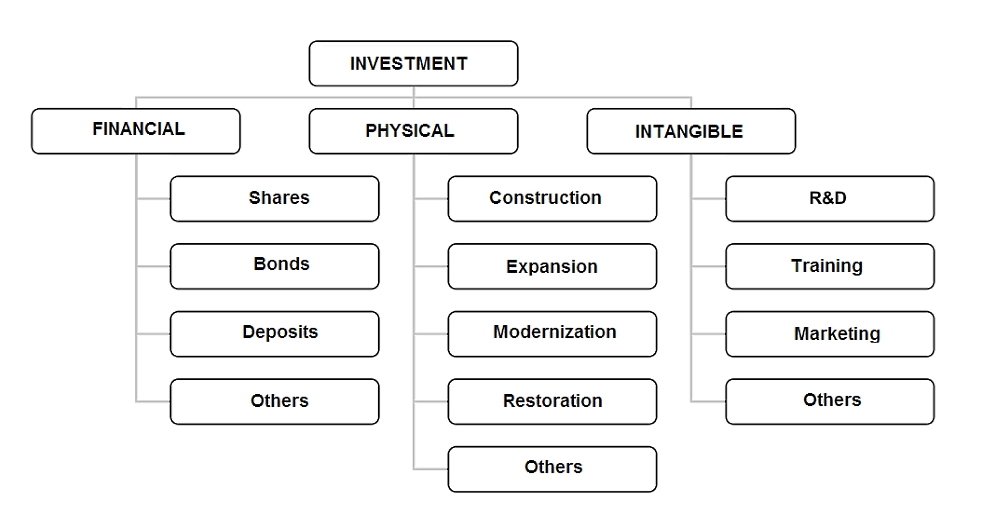
Based on the classical definition of investment as a way of preserving and increasing capital, we can distinguish three broad categories of investment, given below:
• Financial investments: stocks, bonds, deposits, etc.
• Physical investments: any projects in the real sector to create tangible assets.
• Intangible investments: training of company personnel, research and development, patents, various IT systems, advertising and much more.
Figure: Main types of investments.
Physical investments
Physical or real investments are investments made in tangible assets to obtain economic benefits (for example, as a result of an increase in the value of assets or income from production activities).The most common criterion for classifying a physical investment is the purpose or benefits expected from the project. According to this criterion, real investments can be divided into the following broad categories.
An important role in the activities of any enterprise is played by real investments in the modernization of fixed assets, leading to the renewal of production facilities at the current level (replacement of physically or obsolete devices with new ones), as well as investments in business development (expansion of production scale). The latter direction of investment activity contributes to the introduction of new services and products, the development of a sales network and distribution channels.
Also, financial experts identify "replacement" investments aimed at maintaining the existing production capacity, undertaken in order to maintain the company's activities at the current level and maintain a competitive position.
Researchers also highlight strategic investments aimed at protecting the company from adverse conditions, enhancing the company's development in strategically important directions and entering new markets.

A separate category is made up of innovative investments made with the aim of introducing innovative solutions and technologies to the market, regardless of performance criteria, aimed at adapting the company's activities to changing legal norms and current standards. In this type of investment, the goal is not to maximize value for capital owners, but to meet the standards required by law and the market.
Regardless of the goals and type of physical investment, the results of successfully implemented investment projects are usually expressed in the growth of fixed assets of the enterprise.
Experts classify real investment projects by their duration:
• Short-term investments: implementation period up to 3 months, life cycle up to 5 years.
• Medium-term investments: implementation period up to a year, life cycle from 5 to 10 years.
• Long-term investments: implementation period over a year, life cycle over 10 years.
Modern scientific sources subdivide investments according to the type of dependence between projects (for example, complementary projects), sources of financing (the initiator's own funds, loans, subsidies, leasing), the method of project implementation, the type and nature of the benefits received by the parties.
Physical investments are most often carried out with a long-term expectation, therefore, due diligence must be exercised in planning investment costs and sources of their financing, as well as in forecasting financial and economic effects in the future.
The main problems that the company's management must solve when deciding on the investment activities of a business are associated with the uncertainty and low accuracy of forecasting the conditions in which they will be implemented and operated. As the time horizon increases, the project risk increases, and it becomes more difficult for project participants to estimate future costs, interest rates, etc.
Investment project stages
In economic science, an investment project is defined as an event with a strictly defined subject, volume, place and time of its implementation, as well as the cost and projected economic effect of investments.Any investment project consists of several stages listed in the table below.
Table: Stages of the investment project implementation.
| Stages | Actions taken |
| Investment concept | Generation of ideas and their initial assessment, determination of the main parameters of the project, preliminary assessment of the chances of project success, search for alternative investment options and approval of the project. |
| Pre-investment stage | Determination of project viability, preparation of a detailed business plan, calculations and decision on implementation. |
| Facility construction | Obtaining approvals and permits, search and attraction of funds for the implementation of investments, purchase and construction of facilities, conclusion of contracts with construction and service contractors, suppliers of machinery and equipment, testing and commissioning. |
| Operation stage | Conducting production / service activities aimed at obtaining the planned investment income. |
| Completion of the project | Dismantling, utilization, scrapping of machines and devices, leveling and land reclamation, site security. |
The initial phase (intention) includes searching for ideas, initially evaluating them and setting priorities.
At this stage, investment costs and the possibility of financing them are determined, a preliminary analysis of the legal and technical conditions for the implementation of the project, the determination of sales and marketing markets (along with an assessment of demand), a simplified calculation of investment efficiency. Based on numerous studies, the type of project and its possible alternative are determined.
The pre-investment stage consists in the development of an investment project (feasibility study and business plan), including a complex of technical, commercial, financial and organizational aspects of the project and its payback.
In times of economic crisis, this stage requires exceptional attention, given the volatility of markets and significant fluctuations in prices and demand.
The stage of project implementation usually includes the preparation of a technical design and an implementation plan, obtaining the necessary approvals and permits, obtaining funds, negotiating and concluding contracts for the supply, construction or modernization, purchase, leasing and its development (for example, commissioning of machines) and putting the facility into operation.
The operational phase includes the initial operation of the facility, which consists in reaching the design production capacity of the new enterprise, as well as the subsequent standard operation to achieve the set goals and receive the planned return on capital invested by the investors.
The last stage, which is often forgotten in the practice of investment activities, is the stage of completion (closure) of the project.
It consists in the liquidation of an object by selling or writing off tangible assets, their subsequent disposal or protection.
Project phases can overlap over time. While the project may be under construction, some of the phases may already be in operation. The actual start of the project may take place before the completion of all the preparatory work that makes up the pre-investment phase.
Investment costs
Each major investment project has its own characteristics.The use of borrowed funds can be broken down, depending on the specific project, into several stages.
The duration of the pre-investment phase and the construction phase determines how long it will take from the investment decision to the first results.
The time and cost of liquidating a project may vary. Dismantling the technological line, which is built on a specially prepared land plot, reclamation of the site, post-operational protection of open pit mining, disposal of waste and used equipment will require special attention and high costs.
Therefore, each investment project has an individual character and should be considered separately. The external conditions for the implementation of investments are also different. This applies to both the place and the time of the event.
Fiscal policy, the situation on the capital market, the level of interest rates, exchange rate volatility, changes in supply and demand, environmental regulations, labor regulations are just the most important macroeconomic factors affecting the investment activity of a business.
Their clear understanding is necessary for an investor to make a rational investment decision.

Regardless of the differences noted earlier, every investment has a common element. This is the need to bear the financial costs associated with the implementation of the project.
Their structure and size are determined individually for each investment and may include:
• Research and preparation of initial data for the project.
• Purchase of real estate, materials and equipment.
• Raising sufficient funding for success.
• Conclusion of contracts with partners.
Accurate determination of investment costs is the main condition for preparing an investment project.
Budgeting is closely related to this stage.
The project budget is a material and financial plan with an indication of the scope of tasks and the timing of their implementation. It specifies the amount of capital costs required to implement the investment, the procedure and timing for the implementation of stages, the timing of payment for specific tasks. This is the basis for effective investment financing, which can be carried out at the expense of internal or external sources.
Benefits of financial investments for business
The investment activity of a business during a crisis is not only an opportunity for dynamic development, but also often an important condition for the survival of each economic unit.This situation is especially true during periods of deep recession and uncertainty, when the demand for goods decreases, and mainly companies with a formed brand, strong financial position and with the most acceptable product / service for the market survive.
Investment projects are the main tool for creating and improving the production / service potential of the company. This helps the company to meet market expectations and at the same time provides a significant competitive advantage in the period of the subsequent return of the economy to an upward trend.
It is important that during an economic crisis investment costs are usually lower than during a period of dynamic economic growth.
Technologies, materials, and labor in general are cheaper compared to the period when many economic entities compete for them.
However, in practice, companies, fearing for the future, refuse large investments. Difficulties in finding sources of financing, consumer pessimism and uncertainty about the end of the crisis actually block the decision to invest. On the other hand, there is growing concern about capital preservation.
There is an opinion that investments in financial markets do better for this purpose.
The potential benefits of financial investments are summarized below:
• Maintaining the real cost of capital.
• The increase in the market value of assets over time.
• Receiving permanent income in the form of interest or dividends.
• Increased prestige for the transition to other investment instruments.
Financial investment market elements
The range of instruments currently available to investors for investing financial surpluses is very wide.The table below shows the instruments of various segments of the financial market used in investment activities.
Table: Segments of the financial investment market and their features.
| Segment | Short description |
| Money market | This segment includes bank deposits, certificates of deposit, treasury bills, money bills and short-term debt securities. |
| Capital market | Companies invest in stocks, medium and long-term debt securities (treasury or corporate), shares in investment funds, medium and long-term structured financial products and depository receipts. |
| Derivatives market | The derivatives market may include forward or futures contracts, swap options, warrants. |
| Currency market | Investments in this market are associated with foreign exchange transactions, limited by certain periods of execution. |
The most common form of business investment in the financial market is a bank deposit.
However, this does not mean that this financial instrument is reliable in all cases, simple in structure and gives a predetermined financial effect.
In the case of a classic bank deposit with a fixed interest rate for a strictly defined period, the situation is simple. On the one hand, this form of investment is characterized by low investment risk. On the other hand, low interest rates and the loss of part or all of the accrued interest in the event of early closure of the deposit are considered serious drawbacks of bank deposits.
For these reasons, banks offer a number of quasi-deposit instruments, which are most often referred to as structured products. They often give the investor the opportunity to receive a return that is significantly higher than that of a classic bank deposit.
When using these types of instruments, certain conditions must be met by the investor.
They relate to a specific level of exchange rate, stock index, commodity prices on world markets, securities yields, the value of an entire basket of stocks, or the value of investment funds.
However, in the case of structured financial products, the question is not how much the investor will receive under certain conditions, but what happens if the obligations listed in the contract are not met.
The most common offer is a return on the invested amount without investor interest.
Structured financial products are an attractive tool for carrying out investment activities of a business during a crisis. From the point of view of investors, they can be a good alternative to both deposits and physical investments. However, success in this area requires a deep understanding of the essence of this tool and the rational distribution of risks.
The issuers of these financial instruments can be the state treasury, local governments, various enterprises and banks.

Depending on the choice of the debt instrument, the investor strikes a balance between profitability and safety.
Investing in treasury and municipal securities in developed countries means more security, while investing in corporate securities means more profits. However, this claim becomes controversial during a deep crisis that is shaking the financial sector even in stable regions of the world.
The stock exchange provides an investor with an alternative to physical investment.
However, investing in stocks is fraught with the threat of loss of funds, which is not well received by the investment community during the financial crisis. In this case, stock prices do not reflect the real value of the business and are the result of speculative play.
In practice, there are other investment opportunities in the financial markets. Investing in investment funds (including venture capital), currency speculation, buying art, antiques, wine, investing in various indices (securities, commodities) and a wide range of other derivatives offer the investor a valuable alternative to physical investment.
How to invest during the economic crisis
Each economic downturn brings unique investment opportunities, such as buying stocks cheaply on the stock exchange, reduced construction prices, or taking over assets of bankrupt businesses.The Covid-19 pandemic is definitely not the final test for the global economy, so all companies must learn to be flexible in terms of investment policy.
Recent events have spurred the development of the e-commerce industry, while simultaneously hitting tourism, airlines and some real estate markets in traditionally expensive regions of the world. On the one hand, the crisis is costing the global economy trillions of dollars annually. On the other hand, the pandemic is accelerating technological change, innovative business processes and economic transformations that have actually been on the table for many years.
Investing in stock markets is getting easier as we are watching the capital market forever changed thanks to the technological micro-revolution.
Fintech companies are steadily replacing traditional banks by offering modern forms of savings and investment.
There are many alternatives for business. As it becomes more difficult to find attractive forms of investment in the financial markets, interesting prospects have emerged in real estate and the construction industry working for it. Companies that invest correctly in affected industries or discover promising horizons for the future will undoubtedly be in the black.
Any information about the imminent return of the industry to normal life could lead to an increase in the price of shares, for example, of airlines by 100-200% percent in a short time. This applies to hotel chains, restaurants or travel companies.
Sedona Investments, an international financial company from United Kingdom, has assembled a team of highly qualified investment and project finance professionals.
We offer long-term loans, support investment projects and provide a wide range of advisory services in the energy, mining, industry, agriculture, real estate and tourism sectors around the world.













