To consider an application for financing, fill out the form and send it to us by e-mail along with the project brief, or contact our experts
As for investment projects, the United Arab Emirates offers the most attractive conditions for foreign capital among the countries of the Middle East and Africa.
In recent decades, project finance in the UAE has been gaining momentum.
This method of financing large investment projects has attracted the attention of companies around the world, but in the Middle East, the PF has acquired some unique features that are directly related to the historical requirements of Islamic banking.
Despite the fact that project finance in the Arab countries is less developed than in Europe and North America, we see numerous examples of success and significant volumes of project finance in the United Arab Emirates.
The country is moving away from oil dependence, investing huge funds in the development of innovative sectors of the economy, including through the PF and public-private partnerships. According to the results of 2014, EMEA accounted for more than a third of the volume of project finance transactions, and the total value of projects implemented in the region in 2010-2014 exceeded $ 12 billion.
It is not surprising that the energy sector remains the main subject of interest for project finance, followed by industry and the oil and gas sector, as well as financing of road construction and social infrastructure.
One of the most striking examples of PF was the project to expand an aluminum plant in Abu Dhabi: Emirates Aluminum (EMAL), with a total cost of $ 3.6 billion.
A group of energy projects also deserves special attention, including the largest national projects Taweelah A1 and Taweelah A2, Shuweihat-Sl and Umm A1 Nar with a total value of $ 5.4 billion. Each project was aimed at financing expanding combined cycle power plants, reducing waste and reducing the final cost of electricity.
The following institutions have played a special role in the development of project finance in the UAE and the Gulf States:
• General Council for Islamic Banks and Financial Institutions, CIBAFI.
• The Islamic Financial Services Board. The IFSB is an international organization established to develop and enforce global standards for Islamic banking.
• Islamic Development Bank, IsDB (Jeddah, Saudi Arabia). The IDB Group provides project financing on the principles of public-private partnership.
In general, the UAE has great potential for using project finance, especially during the global transition from an oil-based economy.
The PF helps the country to ensure the development of lagging sectors of the economy through the implementation of capital-intensive investment projects with the involvement of foreign partners from around the world.
Distinctive features of project finance in the UAE
The main feature of project finance in the United Arab Emirates comes from the fact that the UAE is an Islamic country that uses distinctive and largely unique tools and models in the financial and banking sectors.There are three types of contracts in Islamic project finance.
Musharaka is used within the bank's operations for export-import financing, project financing and syndications, securities issues that comply with Islamic law.
The basis of musharaka is the joint participation of the bank and the client in the implementation of a business plan (investment plan) and joint financing of this project. The profit is divided in the proportions agreed in advance between the bank and the client. The loss is also divided in proportions corresponding to their participation.
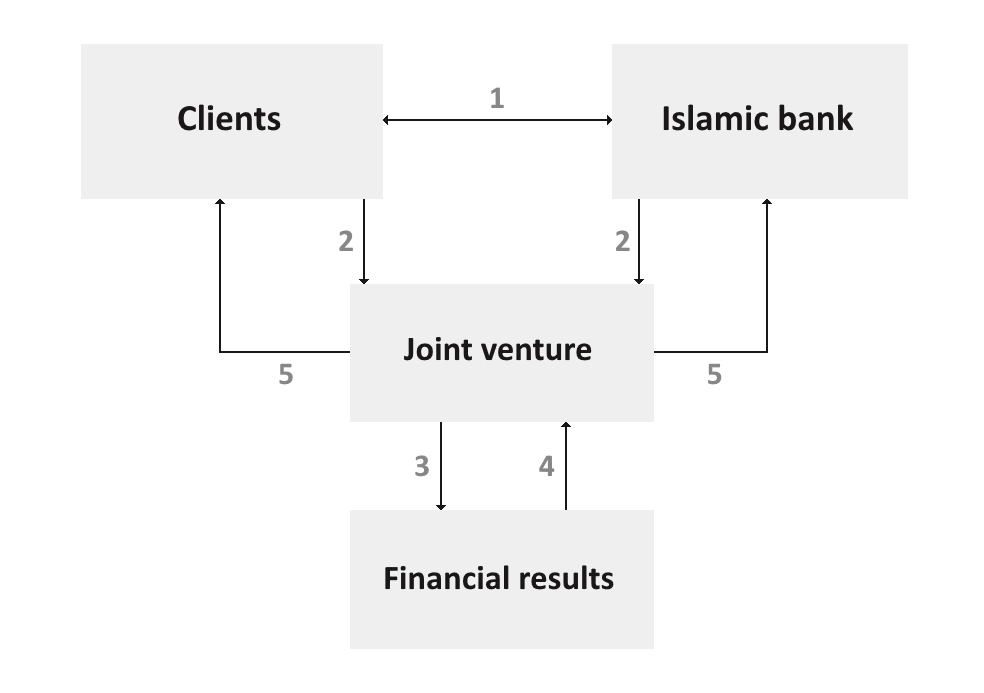
Musharaka is carried out as follows:
1. The bank and the client negotiate the terms of the project and conclude an agreement on joint participation.
2. The parties carry out financing in accordance with the terms of the contract for the implementation of the business project.
3. As part of the project, financial results (profit or loss) are generated.
4. Profits form funds for distribution among participants, and losses reduce the value of assets used to implement the project.
5. The profit (or loss) resulting from the implementation of the business plan is distributed between the bank and the client in pre-agreed proportions.
Mudarabah is widely used for project finance purposes, as well as in syndication and issuance of securities (Sukuk) that comply with Islamic law.
The basis of the partnership is the bank's participation in providing financing for the project. Within the framework of such financing, the bank becomes the "owner of funds", while the bank's client, referred to as a "trusted partner" (mudarib), manages the project, being responsible for the organizational, personnel and technical part of the project.
The profit from the implementation of the project is distributed between the bank and the client in proportions corresponding to the agreements.
Any losses from the project are borne by the bank.
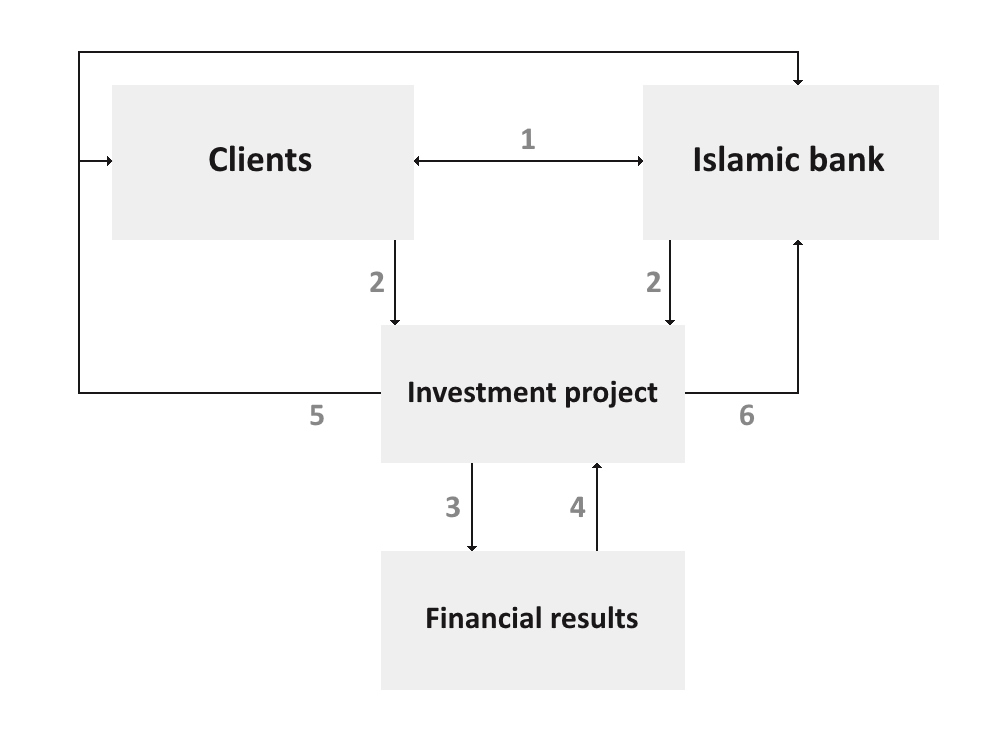
Mudarabah is carried out as follows:
1. The bank and the client enter into a trust partnership agreement for the implementation of an investment project for which the bank provides financing.
2. The client is responsible for the professional management of the project.
3. As a result of the project implementation, financial flows (profit or loss) are generated.
4. Profit creates funds for distribution among project participants, while losses reduce the value of the project's assets.
5. The profit received as a result of the project is distributed between the bank and the client in the agreed proportions.
6. Losses are borne by the financial institution.
Ijarah is used by banks for lease financing and project finance organization.
The basis of ijarah is the temporary transfer of a specific asset to a client (rent, lease). The bank's income is lease payments within the agreed period of use of the above assets.
The main difference between this model of project finance in the UAE from the western model of financial leasing:
• The physical risks associated with the asset are borne by the bank.
• Possibility of subsequent gratuitous transfer of the asset with a minimum residual value.
• Sale of an asset after the end of the lease period as part of a sale transaction.
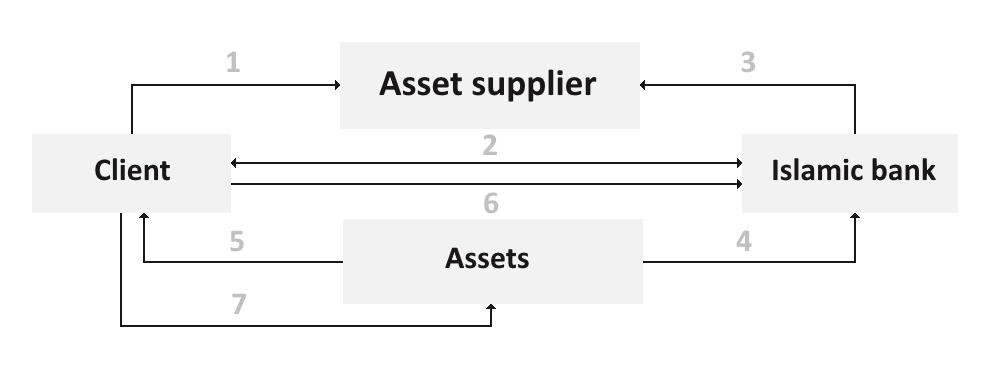
Ijarah is carried out as follows:
1. The client chooses an asset and a supplier for that asset.
2. The client contacts the bank to obtain sufficient funding to use the asset.
3. The bank transfers funds to the supplier of the asset in accordance with the agreement.
4. The supplier transfers the asset into the ownership of the bank.
5. The bank on the basis of the Ijarah transaction provides the client with the acquired asset for a specified period.
6. The customer makes the lease payments for the asset in use.
7. At the end of the lease, the client returns the asset to the bank.
Traditional limitations and risk assessment
When analyzing a company as a borrower, an Islamic bank conducts a business examination and determines the economic potential of this project.If the project meets all the requirements, then the bank makes a decision on participation and concludes an agreement on profit sharing with the client.
It is important to understand that an Islamic bank gives money only for a specific project. Another feature is the ban on futures. No game can be played with products that have not yet been created. It is also impossible to speculate on various derivatives, because "making money out of thin air" is not allowed in Islamic banking.
Project finance in the UAE, like the entire financial sector, operates in accordance with the rules of Islamic banking and finance, which include the following:
• Prohibition on transactions with conditions of uncertainty (gharar).
• The prohibition on interest rate as an exploitative source of income: money on debt at interest (riba nasiah) and unequal exchange (riba fadl).
• Restrictions on financing certain sectors of the economy, such as gambling, the production of pork and its products, alcoholic beverages, etc.
• Conditions for fair sharing of risk and profit (loss) between the bank and the client for any transactions performed.
• Execution of financial transactions only on the basis of real assets or transactions with these assets.

Each project is characterized by the following main parameters.
These are the goal (result), the cost and budget of the project, and the life cycle of the project. The project analysis is necessarily carried out by a financial institution in order to make a decision on participation in the project (form of participation, instruments, the cost of financing instruments used). The actual examination of an investment project in the UAE is a process that, in some respects, is difficult for Western entrepreneurs to understand.
This analysis should confirm the compliance of the project with the requirements of Islamic banking, which are reflected in the bank's investment policy and relevant regulatory documents.
At the stage of examination, an Islamic bank, carrying out a project analysis, develops an optimal financing plan and a contractual structure for sharing project risks. When deciding on project financing, Islamic banks are guided, like ordinary banks, by the guarantees provided by the client.
Sedona Investments has significant experience in organizing project finance in the United Arab Emirates and other countries in the Middle East.
We are ready to help your business in the implementation of large investment projects of any complexity, guaranteeing a professional approach and high-quality legal support.
Please contact our representatives at any time for details.













